 |
| April 14, 2020 | Volume 16 Issue 14 |
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Self-powered X-ray detector to revolutionize imaging for medicine, security, and research
A new X-ray detector prototype is on the brink of revolutionizing medical imaging, with a dramatic reduction in radiation exposure and the associated health risks. The invention could also boost the resolution in security scanners and research applications. It was all made possible thanks to a collaboration between Los Alamos National Laboratory and Argonne National Laboratory researchers.
"The perovskite material at the heart of our detector prototype can be produced with low-cost fabrication techniques," said Hsinhan (Dave) Tsai, an Oppenheimer Postdoctoral fellow at Los Alamos National Laboratory. "The result is a cost-effective, highly sensitive, and self-powered detector that could radically improve existing X-ray detectors, and potentially lead to a host of unforeseen applications."
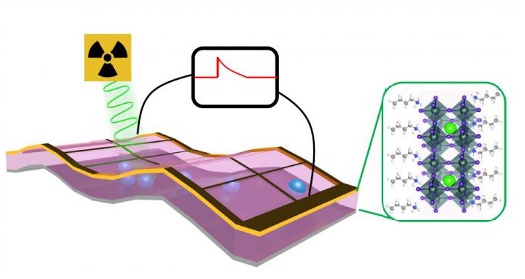
X-ray detectors made with two-dimensional perovskite thin films convert X-ray photons to electrical signals without requiring an outside power source, and are 100 times more sensitive than conventional detectors. [Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory]
The detector replaces silicon-based technology with a structure built around a thin film of the mineral perovskite, resulting in a hundred times more sensitivity than conventional silicon-based detectors. In addition, the new perovskite detector does not require an outside power source to produce electrical signals in response to X-rays.
High-sensitivity perovskite detectors could enable dental and medical images that require a tiny fraction of the exposure that accompanies conventional X-ray imaging. Reduced exposure decreases risks for patients and medical staff alike. The fact that perovskite detectors can be made very thin allows them to offer increased resolution for highly detailed images, which will lead to improved medical evaluations and diagnoses. Lower-energy and increased-resolution detectors could also revolutionize security scanners and imaging in X-ray research applications.
Because perovskite is rich in heavy elements, such as lead and iodine, X-rays that easily pass through silicon undetected are more readily absorbed and detected in perovskite. As a result, perovskite significantly outperforms silicon, particularly at detecting high-energy X-rays. This is a crucial advantage when it comes to monitoring X-rays at high-energy research facilities, such as synchrotron light sources.
Perovskite films can be deposited on surfaces by spraying solutions that cure and leave thin layers of the material behind As a result, the thin-layer detectors will be much easier and cheaper to produce than silicon-based detectors, which require high-temperature metal deposition under vacuum conditions.
"Potentially, we could use ink-jet types of systems to print large-scale detectors," said Tsai. "This would allow us to replace half-million-dollar silicon detector arrays with inexpensive, higher-resolution perovskite alternatives."
In addition to the promise of thin-layer perovskites in X-ray detectors, thicker layers work well provided they include a small voltage source. This suggests that their useful energy range could be extended beyond X-rays to low-energy gamma-rays.
The new prototype was fabricated and tested successfully thanks to a collaborative effort among Los Alamos National Laboratory material scientists led by Wanyi Nie and Hsinhan Tsai, and the Los Alamos Theory team led by Sergei Tretiak, in conjunction with Joseph Strzalka at Argonne National Laboratory's X-ray Science Division.
Source: Los Alamos National Laboratory
Published April 2020
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
